| CPC H04W 8/04 (2013.01) [H04W 8/12 (2013.01); H04W 8/28 (2013.01); H04W 12/06 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
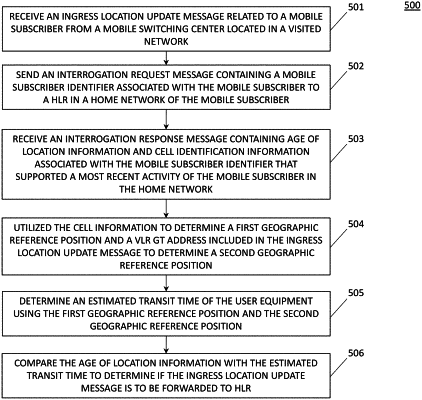
1. A method for conducting a velocity check for outbound subscribers roaming to neighboring countries, the method comprising:
receiving, by a network gateway associated with a home network located in a home country from a mobile switching center (MSC) associated with a visited network located in a foreign country that neighbors the home country, an ingress signaling message related to a mobile device roaming in the visited network;
determining from a country code identifier included in the ingress signaling message that the foreign country is a neighboring country to the home country;
conducting a velocity check of the mobile device based on the determination that the foreign country is a neighboring country, wherein conducting the velocity check comprises:
sending, to a home location register (HLR) in the home network, an interrogation request message containing a mobile subscriber identifier associated with the mobile device;
receiving an interrogation response message containing age of location information and cell identifier information corresponding to the mobile subscriber identifier;
utilizing the cell identifier information to determine a first geographic reference position and the country code identifier included in the ingress signaling message to determine a second geographic reference position;
determining an estimated transit time of the mobile device using the first geographic reference position and the second geographic reference position; and
comparing age of location information with the estimated transit time to determine if the ingress signaling message is to be forwarded to the HLR.
|