| CPC G06N 7/01 (2023.01) [G06N 20/00 (2019.01); G07C 9/27 (2020.01); G07C 9/37 (2020.01)] | 22 Claims |
|
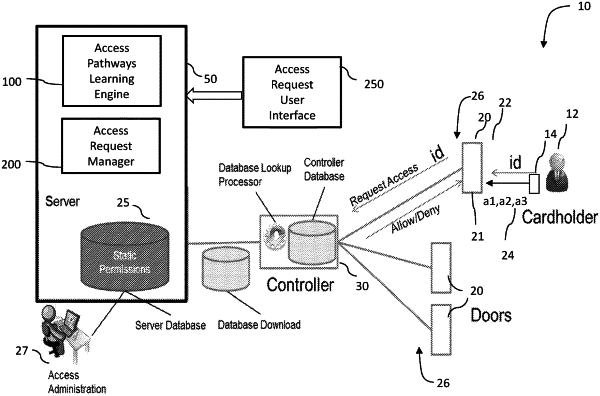
1. An access control request manager based on learning profile based access pathways in a physical access control system (PACS), the access control request manager comprising:
an access pathways learning module configured to determine a reachability graph associated with each resource in the PACS;
a permissions request module in operable communication with the access pathways learning module, the permissions request module including an access request user interface configured to permit a user or an administrator, to provide a request for a permission to permit the user access to, or revoke the user's access to, a resource in the PACS, the permissions request module configured to:
determine if the requested permission is already granted to the user;
compute a pathway to reach the requested resource based on the reachability graph;
suggest a permission, if needed, required to satisfy the request based on the computed pathway; and
if approved, add the suggested permission to any permissions granted to the user;
wherein the reachability graph is based on a statistical rule that a first reader can be reached from a second reader if there exists two consecutive access events in a history of access events for any cardholder that accesses the first reader and the second reader.
|