| CPC G04F 5/145 (2013.01) [G01N 21/645 (2013.01); G04F 5/14 (2013.01); H03L 7/26 (2013.01); G01N 2021/6471 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A frequency-modulation spectroscopy process comprising:
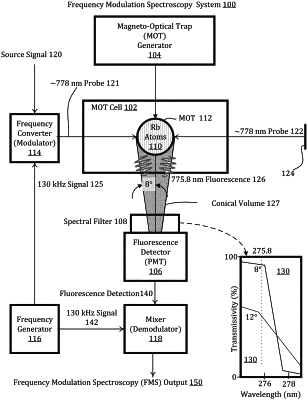
forming an optical trap to localize molecular entities in a subregion of a cell, the subregion having a volume that is less than 1/10 of an internal volume of the cell;
frequency converting an optical source signal to provide a first probe beam having a first probe wavelength, the frequency conversion including frequency modulating the optical source signal using a radio-frequency signal;
probing the molecular entities using at least the first probe beam so that the molecular entities emit fluorescence having a first fluorescence wavelength different from the first probe wavelength;
spectrally filtering the fluorescence using a spectral filter, the spectral filter being characterized by an effective angle of incidence on the spectral filter within which the spectral filter can effectively block the first probe wavelength and transmit the first fluorescence wavelength, the filter being less effective at blocking the first probe wavelength or transmitting the first fluorescence wavelength at angles larger than the effective angle of incidence, at least half of the molecular entities that emit the fluorescence being within a conical volume defined by the effective angle of incidence;
detecting the spectrally filtered fluorescence transmitted by the spectral filter to provide a fluorescence detection signal; and
demodulating the fluorescence detection signal so as to provide a frequency-modulation spectroscopy output signal.
|