| CPC A61B 5/4806 (2013.01) [A61B 5/377 (2021.01); A61B 2560/02 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
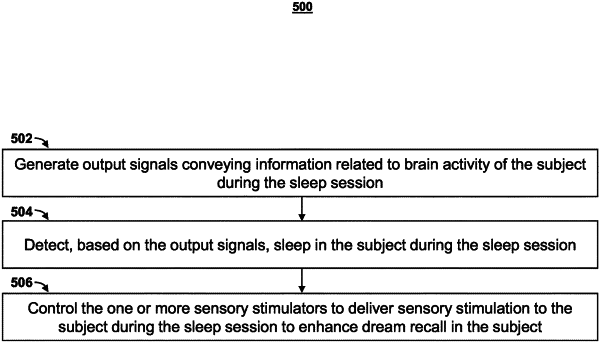
1. A system for enhancing dream recall in a subject, the system comprising:
one or more sensors configured to generate output signals conveying information related to brain activity of a subject during a sleep session;
one or more sensory stimulators configured to provide sensory stimulation to the subject; and
one or more processors operatively coupled to the one or more sensors and the one or more sensory stimulators, the one or more processors configured by machine-readable instructions to:
detect, based on the output signals, rapid eye movement (REM) sleep in the subject during the sleep session;
control the one or more sensory stimulators to deliver the sensory stimulation to the subject during the REM sleep to enhance the dream recall in the subject;
determine, based on the output signals, an electroencephalogram (EEG) for the subject during the sleep session;
determine a theta power for the EEG; and
control the one or more sensory stimulators to deliver the sensory stimulation to the subject during the REM sleep to enhance the EEG theta power, the enhanced EEG theta power being associated with the dream recall in the subject, wherein, to control the one or more sensory stimulators to deliver the sensory stimulation to the subject during the REM sleep to enhance the EEG theta power, the one or more processors are further configured to:
detect, based on the output signals, an increase in the EEG theta power associated with the subject during the REM sleep; and
cause the one or more sensory stimulators to deliver the sensory stimulation to the subject at a constant intensity based on the detected increase in the EEG theta power.
|