| CPC A61B 5/372 (2021.01) [A61B 5/291 (2021.01); A61B 5/31 (2021.01); A61B 5/4094 (2013.01); A61B 5/7246 (2013.01)] | 16 Claims |
|
1. A computer-implemented method for detecting brain activity patterns from a scalp electroencephalographic signal, the method comprising the steps of:
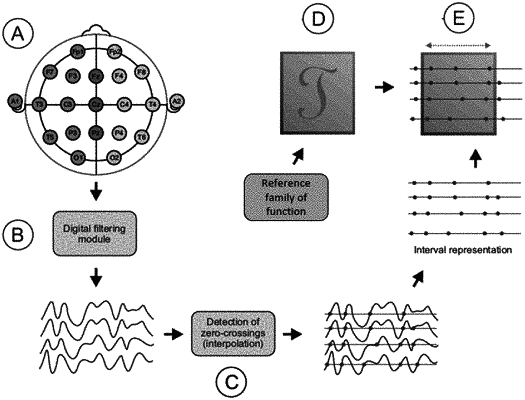
a) obtaining electroencephalographic signals as a function of multiple channels and time;
b) identifying, for each channel, the zero-crossings of its corresponding electroencephalographic signal over a fixed threshold;
c) generating a zero-crossing representation of the electroencephalographic signals with the identified zero-crossings;
d) obtaining at least one reference family of functions of time and channels from a zero-crossing statistical analysis of a zero-crossing representation of pre-recorded electroencephalographic signals, the functions of the at least one reference family of functions being real functions;
e) for each segment of a plurality of segments of the generated zero-crossing representation, calculating a corresponding matching score by comparing said zero-crossing representation of the segment with at least one reference function from the at least one reference family of functions;
f) monitoring an evolution of the matching score over time based on a set of matching scores for successive segments of the generated zero-crossing representation;
wherein, for each segment, the corresponding matching score relative to a zero-crossing representation of a segment for one reference function T centered in t0 is defined by the formula:
ST(t0)=Σk εKΣtεϕ(k,t0)Tk(t−t0),
wherein ST(t0) is the matching score, the first sum runs over the set of channels k εK, and the second sum runs over a defined subset t εϕ(k, t0) of zero-crossings for each channel k of the segment surrounding t0; and
g) determining a state of the brain based on the evolution of the matching score.
|