| CPC H04L 41/0654 (2013.01) [H04L 45/24 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
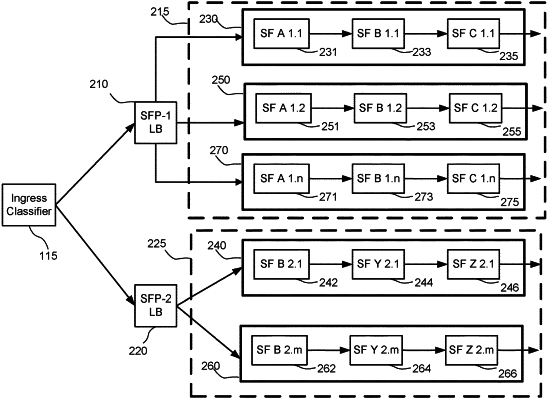
1. A method for processing a packet flow in a service function path (SFP), the method comprising:
receiving, by a network function, a first packet in the packet flow, the first packet including an indication identifying a primary SFP instance assigned to the packet flow, wherein the network function is associated with the primary SFP instance in a set of SFP instances;
updating, by the network function, a packet flow-related service function (SF) state associated with the packet flow according to the first packet;
determining, by the network function, a backup network function, the network function and the backup network function communicatively coupled to synchronize the packet flow-related SF state, the backup network function associated with a second SFP instance in the set of SFP instances, wherein the second SFP instance is determined based on the indication identifying the primary SFP instance for the packet flow; and
sending, by the network function to the backup network function, a state update message comprising the packet flow-related SF state associated with the packet flow,
wherein the state update message is transmitted in a state update packet, the state update packet including an indication of a number of instances in the set of SFP instances, an indication identifying the primary SFP instance associated with the network function, an indication identifying the second SFP instance associated with the backup network function, a unicast source address associated with the network function, and a unicast destination address associated with the backup network function, the destination address derived from the indication identifying the second SFP instance associated with the backup network function.
|