| CPC G06F 30/398 (2020.01) [G06F 30/392 (2020.01); G06F 2111/04 (2020.01); G06F 2117/10 (2020.01); G06F 2119/12 (2020.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
1. A system comprising:
one or more processors of a machine; and
at least one computer storage medium storing instructions, which, when executed by the machine, cause the machine to perform operations comprising:
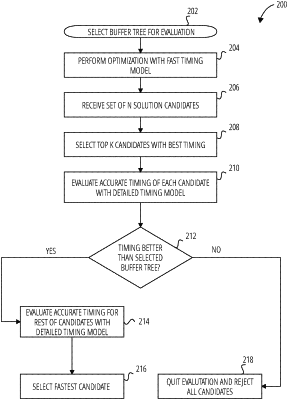
accessing a circuit design stored in memory, the circuit design comprising a buffer tree having a baseline timing characteristic;
identifying a set of candidate solutions for improving the baseline timing characteristic using an initial timing model;
selecting, based on the initial timing model, a subset of candidate solutions from the set of candidate solutions that have a timing characteristic lower than the baseline timing characteristic;
evaluating the subset of candidate solutions using a secondary timing model;
based on determining that at least one candidate solution in the subset of candidate solutions has a timing characteristic that is better than the baseline timing characteristic of the buffer tree, evaluating a remainder of candidate solutions from the set of candidate solutions using the secondary timing model;
selecting, a faster candidate solution after evaluating the set of candidate solutions using the secondary timing model; and
replacing a portion of the buffer tree with the faster candidate solution.
|