| CPC B41J 3/28 (2013.01) [B41J 2/04505 (2013.01); B41J 2/17596 (2013.01)] | 28 Claims |
|
1. An apparatus for printing fluid on a printable surface of a substrate, comprising:
a substrate stage relative to which the substrate is fixed in position during the printing;
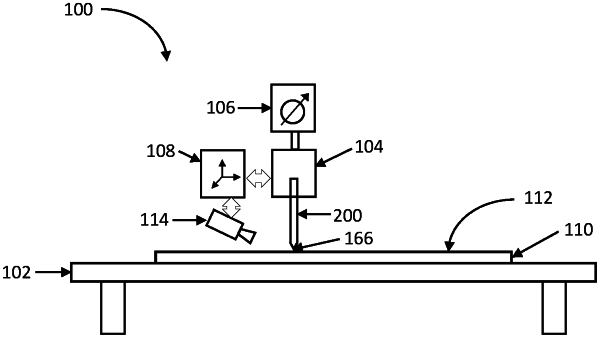
a print head positioned above the substrate and comprising a micro-structural fluid ejector, the micro-structural fluid ejector comprising: (1) an output portion comprising an exit orifice of an output inner diameter ranging between 0.1 μm and 5 μm and an end face having a surface roughness of less than 0.1 μm, (2) an elongate input portion having an input inner diameter that is greater than the output inner diameter by a factor of at least 100, and (3) a tapering portion between the elongate input portion and the output portion;
a pneumatic system coupled to the print head such that the pneumatic system applies pressure to the fluid in the micro-structural fluid ejector via the elongate input portion, the pressure being regulated to within a range of −50,0000 Pa to 1,000,000 Pa during the printing; and
a print head positioning system which controls a vertical displacement and a lateral displacement of the print head relative to the substrate;
wherein the micro-structural fluid ejector is oriented with the output portion pointing downward and the end face facing toward the printable surface;
the print head positioning system maintains a vertical distance between the end face and the printable surface within a range of 0 μm to 5 μm during the printing;
the print head ejects fluid through the exit orifice in a continuous stream without any applied electric field between the print head and the substrate, the continuous stream forming a line of fluid on the printable surface.
|