| CPC A61B 8/4254 (2013.01) [A61B 8/469 (2013.01); A61B 8/485 (2013.01); A61B 8/5261 (2013.01); A61B 90/36 (2016.02); G06T 7/0014 (2013.01); A61B 8/463 (2013.01); A61B 8/58 (2013.01); A61B 2034/2051 (2016.02); A61B 2090/364 (2016.02); A61B 2090/365 (2016.02); A61B 2090/378 (2016.02); G06T 7/0012 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A medical image fusion system comprising:
a computer capable of processing medical images;
a source of previously acquired reference images, the images comprising a region of interest (ROI) in a body, the ROI including an organ having a surface;
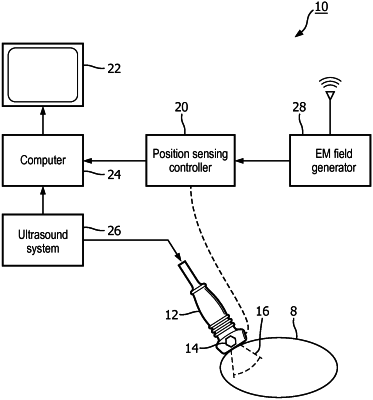
an ultrasound system comprising an internal probe and configured to acquire from within the body ultrasound images;
a spatial tracking system, coupled to the internal probe, and arranged to track the spatial location of the internal probe during image acquisition;
wherein the computer is adapted to align the ultrasound images acquired by the ultrasound system and the reference images, based, at least in part, on minimizing an energy value calculated from a global transformation and a local deformation,
wherein the computer is further adapted to determine from the tracked internal probe location whether the internal probe location is at least partially inside the surface of the organ shown in a spatially corresponding reference image, and, if so,
wherein the computer is further adapted to modify the reference image, wherein the modifying of the reference image comprises:
displaying the internal probe location outside the surface of the organ shown in the reference image;
redrawing the surface shown in the reference image;
recasting the appearance of tissue in the reference image so that the tissue is contained within the redrawn surface; and
deforming the appearance of tissue in front of the internal probe location and inside the redrawn surface of the organ in the reference image based, at least in part, on the global transformation and the local deformation, wherein deforming is performed in consideration of a gradient of a density and/or a stiffness of the tissue,
wherein the gradient is over a distance between the tissue and the internal probe,
wherein the organ is at least one of an abdominally scanned organ or a prostate.
|