| CPC A61B 5/024 (2013.01) [A61B 5/004 (2013.01); A61B 5/0255 (2013.01); A61B 5/1128 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A computer-implemented method of monitoring vital signs comprising:
in a digital processor:
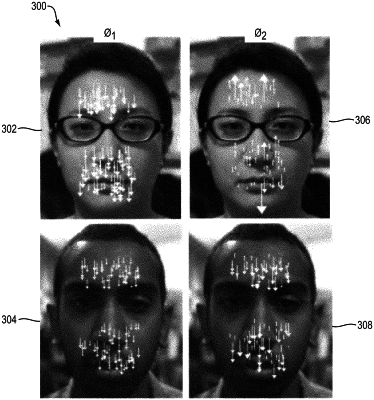
receiving an input video of an upper body portion of a subject, the input video being formed of a sequence of frames, each frame: (i) providing a respective image of the upper body portion, (ii) having spatial locations corresponding to feature points in the image, and (iii) representing a data point in a position-time series of the sequence of frames, each location being a pixel representing visible light spectrum;
forming a location-time series returning the spatial locations of each feature point across plural frames of the input video; and
from the formed location-time series and the position-time series, detecting a pulse signal and extracting pulse rate measurements, said extracting including output of a pulse rate or a heart rate of the subject shown in the video.
|