| CPC H02M 7/5395 (2013.01) [G01R 19/16538 (2013.01); H02M 1/32 (2013.01); H02M 1/0009 (2021.05); H02M 1/0058 (2021.05); H02M 1/327 (2021.05); H02M 7/4818 (2021.05)] | 5 Claims |
|
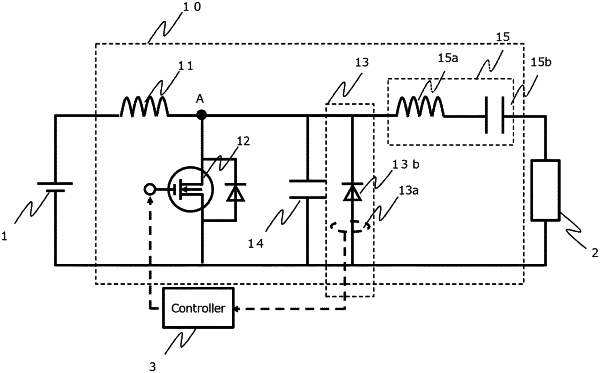
1. A control method of controlling a resonance type power conversion device including a voltage resonance circuit, the method comprising:
providing the voltage resonance circuit, which comprises:
a choke coil connected to an input power supply,
a first switching element connected to the choke coil,
a capacitor connected in parallel to the first switching element,
a resonance circuit connected between a connection point and an output terminal, the connection point being a point at which the choke coil and the first switching element are connected, and
a parallel circuit connected in parallel to the first switching element, wherein:
the parallel circuit includes a diode connected between a lower potential side of the first switching element and the connection point, and
a conductive direction of the diode is a direction in which a forward direction current flows from a lower potential side of the first switching element to the connection point;
detecting, by a sensor, a polarity of a diode current flowing to the diode in a state in which the first switching element is turned on at a timing of a predetermined period;
when the forward direction current flows to the diode, making a timing for turning on the first switching element later than the timing of the predetermined period; and
when the diode current is not flowing, making the timing for turning on the first switching element earlier than the timing of the predetermined period.
|