| CPC G06T 7/344 (2017.01) [A61B 34/10 (2016.02); G06T 7/11 (2017.01); G06T 7/337 (2017.01); G06T 17/00 (2013.01); G06T 19/20 (2013.01); A61B 34/20 (2016.02); A61B 2034/102 (2016.02); A61B 2034/105 (2016.02); A61B 2090/367 (2016.02); A61B 2090/3762 (2016.02); G06T 2207/10081 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10124 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30008 (2013.01); G06T 2210/41 (2013.01); G06T 2219/2004 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
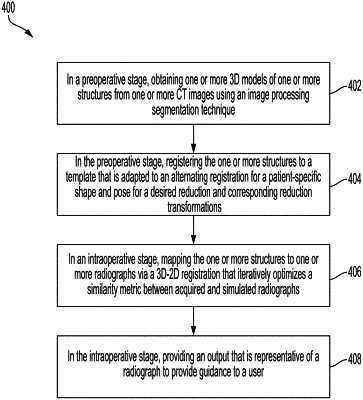
1. A method for registering one or more structures to a desired orientation for planning and guidance for surgery, the method comprising:
in a preoperative stage, obtaining one or more 3D models of one or more structures from one or more CT images using an image processing segmentation technique or a manual segmentation technique;
in the preoperative stage, registering the one or more structures to a template that is adapted to an alternating registration for a patient-specific shape and pose for a desired reduction and corresponding reduction transformations, wherein the registering comprises computing a cost function for multi-body registration based on a disparity between the template and positions of the one or more structures and wherein the cost function is further computed based on a fragment collision regularization;
in an intraoperative stage, mapping the one or more structures to one or more radiographs via a 3D-2D registration that iteratively optimizes a similarity metric between acquired and simulated radiographs; and
in the intraoperative stage, providing an output that is representative of a radiograph or a 3D tomographic representation to provide guidance to a user.
|