| CPC F02D 13/04 (2013.01) [F01L 13/065 (2013.01); F02B 37/24 (2013.01); F02D 13/0249 (2013.01); F02D 41/2422 (2013.01); F02B 2037/122 (2013.01); F02D 2200/0406 (2013.01); F02D 2200/101 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
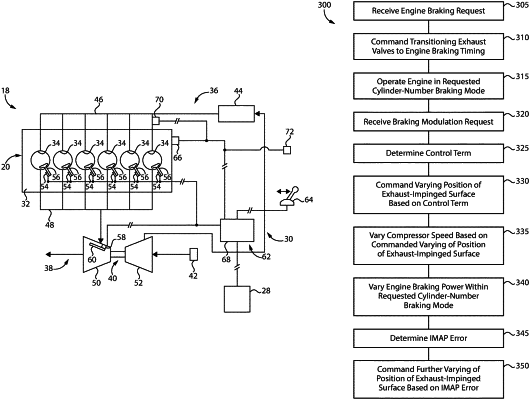
1. A method of braking an engine comprising:
operating an engine in a cylinder-number braking mode where exhaust valves for some combustion cylinders in the engine are operated in an engine braking timing pattern and exhaust valves for some combustion cylinders in the engine are operated in a combustion timing pattern;
determining a control term indicative of at least one of an intake air pressure different from a present intake air pressure or a change to an intake air pressure from a present intake air pressure, that varies a braking power of the engine;
commanding varying a position of an exhaust-impinged surface in an exhaust turbine for the engine based on the determined control term;
varying a speed of an intake air compressor for the engine driven by the exhaust turbine, based on the commanded varying of a position of the exhaust-impinged surface; and
decreasing the braking power of the engine, within the cylinder-number braking mode, based on a decrease to intake air pressure in the engine occurring in response to the varied speed of the intake air compressor; and
the decreasing the braking power including decreasing the braking power via closed loop control using intake air pressure as a targeted variable.
|