| CPC C25B 3/23 (2021.01) [B01J 27/13 (2013.01); C25B 11/02 (2013.01); C25B 11/04 (2013.01); C25B 15/02 (2013.01); C25B 15/08 (2013.01); C07C 31/04 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
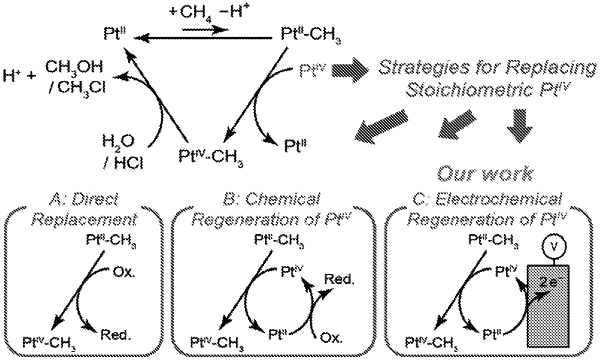
1. A process for oxidizing a compound, comprising:
(i) providing a reaction mixture, comprising water, a PtII species at an initial concentration, a compound of formula R1-R2, an anion, and a Bronsted acid;
(ii) applying an electrical current to the reaction mixture at a temperature, thereby oxidizing the compound of formula R1-R2;
(iii) measuring a reaction concentration of the PtII species in the reaction mixture; and
(iv) modulating the electrical current in situ to maintain the reaction concentration of the PtII species during the process at about 95% to about 105% of the initial concentration;
wherein
the anion is chloride, fluoride, bromide, iodide, a carboxylate, nitrate, perchlorate, phosphate, or sulfate;
the initial concentration of PtII species is about 1 mM to about 10 M;
R1 is C1-C20 alkyl, C3-C12 cycloalkyl, C5-C10 heterocyclyl, C6-C12 aryl, or C5-C12 heteroaryl; and
R2 is H, —OH, —C(═O)H, or —C(═O)OH.
|