| CPC A61N 1/3622 (2013.01) [A61N 1/3624 (2013.01); A61N 1/36507 (2013.01); A61N 1/37217 (2013.01); A61N 1/3987 (2013.01); A61N 1/39622 (2017.08); A61N 1/3756 (2013.01); A61N 1/37512 (2017.08); A61N 1/3918 (2013.01)] | 21 Claims |
|
1. A medical device comprising:
a sensing circuit configured to receive a cardiac electrical signal;
a control circuit coupled to the sensing circuit and configured to:
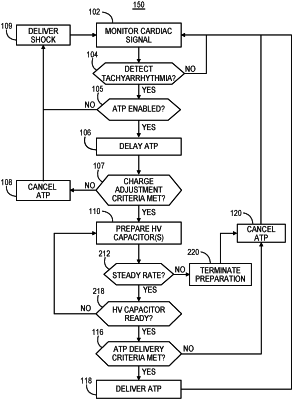
detect a tachyarrhythmia from the cardiac electrical signal; and
start an anti-tachycardia pacing (ATP) therapy delay period in response to detecting the tachyarrhythmia; and
a therapy delivery circuit coupled to the control circuit, the therapy delivery circuit comprising a high voltage capacitor chargeable to a shock voltage amplitude for delivering a cardioversion/defibrillation shock pulse; the therapy delivery circuit configured to:
adjust a charge of the high voltage capacitor to a pacing voltage amplitude during the ATP therapy delay period, the pacing voltage amplitude being less than the shock voltage amplitude.
|
|
11. A method comprising:
receiving a cardiac electrical signal;
detecting a tachyarrhythmia from the cardiac electrical signal;
starting an anti-tachycardia pacing (ATP) therapy delay period in response to detecting the tachyarrhythmia; and
adjusting a charge of a high voltage capacitor to a pacing voltage amplitude during the ATP therapy delay period, wherein the high voltage capacitor is chargeable to a shock voltage amplitude for delivering a cardioversion/defibrillation shock pulse and the pacing voltage amplitude is less than the shock voltage amplitude.
|