| CPC A61M 15/001 (2014.02) [A61M 15/002 (2014.02); A61M 15/0085 (2013.01); B05B 12/08 (2013.01); B05B 17/0646 (2013.01); B05B 17/0661 (2013.01); B05B 17/0669 (2013.01); B05B 17/0684 (2013.01); A61M 15/06 (2013.01); A61M 2205/3368 (2013.01); A61M 2205/3375 (2013.01); A61M 2205/8206 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
1. A mist inhaler device for generating a mist containing a therapeutic for inhalation by a user, the device comprising:
a mist generator device which incorporates:
a mist generator housing which is elongate and comprises an air inlet port and a mist outlet port;
a liquid chamber provided within the mist generator housing, the liquid chamber containing a liquid to be atomised, the liquid comprising a therapeutic;
a sonication chamber provided within the mist generator housing;
a capillary element extending between the liquid chamber and the sonication chamber such that a first portion of the capillary element is within the liquid chamber and a second portion of the capillary element is within the sonication chamber;
an ultrasonic transducer having an atomisation surface, wherein part of the second portion of the capillary element is superimposed on part of the atomisation surface, and wherein when the ultrasonic transducer is driven by an AC drive signal the atomisation surface vibrates to atomise the liquid carried by the second portion of the capillary element to generate a mist comprising the atomised liquid and air within the sonication chamber; and
an airflow arrangement which provides an air flow path between the air inlet port, the sonication chamber and the mist outlet port such that a user drawing on the mist outlet port draws air through the inlet port, through the sonication chamber and out through the mist outlet port, with the mist generated in the sonication chamber being carried by the air out through the mist outlet port for inhalation by the user, wherein the mist inhaler device further comprises:
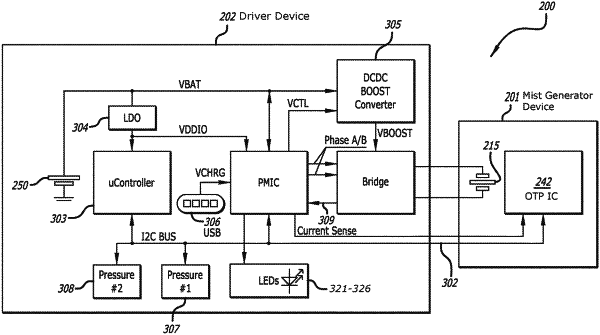
a driver device which incorporates:
a battery;
an H-bridge circuit which is connected to the ultrasonic transducer, wherein the H-bridge circuit generates an AC drive signal to drive the ultrasonic transducer;
a microchip connected to the H-bridge circuit to control the H-bridge circuit to generate the AC drive signal, wherein the microchip is a single unit which comprises a plurality of interconnected embedded components and subsystems comprising:
an oscillator which generates:
a main dock signal,
a first phase dock signal which is high for a first time during the positive haft-period of the main dock signal and low during the negative haft-period of the main dock signal, and
a second phase dock signal which is high for a second time during the negative half-period of the main dock signal and low during the positive haft-period of the main dock signal, wherein phases of the first phase dock signal and the second phase dock signal are centre aligned;
a pulse width modulation (PWM) signal generator subsystem comprising:
a delay locked loop which generates a double frequency clock signal using the first phase dock signal and the second phase dock signal, the double frequency clock signal being double the frequency of the main dock signal, wherein the delay locked loop controls a rising edge of the first phase dock signal and the second phase dock signal to be synchronous with a rising edge of the double frequency clock signal, and wherein the delay locked loop adjusts the frequency and the duty cycle of the first phase dock signal and the second phase dock signal in response to a driver control signal to produce a first phase output signal and a second phase output signal, wherein the first phase output signal and the second phase output signal are configured to drive the H-bridge circuit to generate an AC drive signal to drive the ultrasonic transducer;
a first phase output signal terminal which outputs the first phase output signal to the H-bridge circuit;
a second phase output signal terminal which outputs the second phase output signal to the H-bridge circuit;
a feedback input terminal which receives a feedback signal from the H-bridge circuit, the feedback signal being indicative of a parameter of the operation of the H-bridge circuit or AC drive signal when the H-bridge circuit is driving the ultrasonic transducer with the AC drive signal to atomise the liquid;
an analogue to digital converter (ADC) subsystem comprising:
a plurality of ADC input terminals which receive a plurality of respective analogue signals, wherein one ADC input terminal of the plurality of ADC input terminals is connected to the feedback input terminal such that the ADC subsystem receives the feedback signal from the H-bridge circuit, and wherein the ADC subsystem samples analogue signals received at the plurality of ADC input terminals at a sampling frequency which is proportional to the frequency of the main clock signal and the ADC subsystem generates ADC digital signals using the sampled analogue signals;
a digital processor subsystem which receives the ADC digital signals from the ADC subsystem and processes the ADC digital signals to generate the driver control signal, wherein the digital processor subsystem communicates the driver control signal to the PWM signal generator subsystem to control the PWM signal generator subsystem; and
a digital to analogue converter (DAC) subsystem comprising:
a digital to analogue converter (DAC) which converts a digital control signal generated by the digital processor subsystem into an analogue voltage control signal to control a voltage regulator circuit which generates a voltage for modulation by the H-bridge circuit; and
a DAC output terminal which outputs the analogue voltage control signal to control the voltage regulator circuit to generate a predetermined voltage for modulation by the H-bridge circuit to drive the ultrasonic transducer in response to feedback signals which are indicative of the operation of the ultrasonic transducer.
|