| CPC H04L 63/1416 (2013.01) | 17 Claims |
|
1. An apparatus comprising:
one or more processors operable to execute stored instructions that, when executed, cause the one or more processors to:
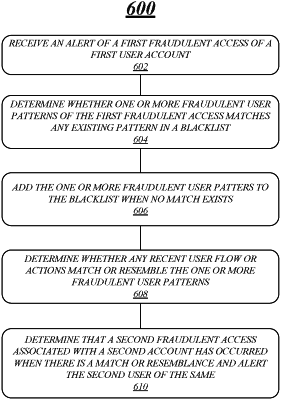
determine a first fraudulent user pattern in response to a notification from a first user account of a first fraudulent access, the first fraudulent user pattern comprising a fraudster sequentially performing a first action and a second action via an account interface;
add the first fraudulent user pattern to a blacklist;
determine a second fraudulent user pattern indicating an abnormal user pattern likely to be fraudulent, the second fraudulent user pattern being determined without notification from any user account;
dynamically update the blacklist to add the second fraudulent user pattern and generate an updated blacklist;
perform a fraud analysis by analyzing a plurality of user accounts by comparing at least the first and second fraudulent user patterns of the blacklist to user account activities associated with the plurality of user accounts;
detect that a second fraudulent access associated with a second user account has occurred based on the performed fraud analysis; and
alert the second user account of the second fraudulent access,
wherein the determination of the second fraudulent user pattern comprises the one or more processors to:
detect that the abnormal user pattern likely to be fraudulent is similarly or identically associated with multiple user accounts;
perform a second fraud analysis by analyzing the abnormal user pattern across the multiple accounts; and
determine that there is a probability that the multiple accounts are being fraudulently accessed by a same fraudster based at least in part on the performed second fraud analysis.
|