| CPC H01M 8/188 (2013.01) [H01M 8/18 (2013.01); Y02E 60/50 (2013.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
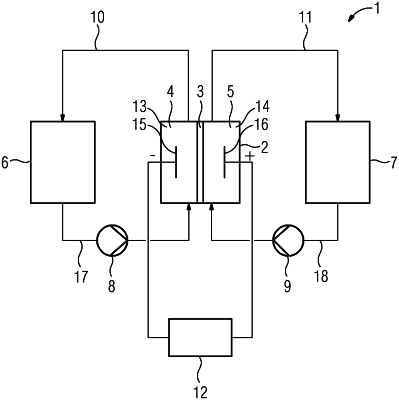
1. A method for operating an electrically rechargeable redox flow battery, the method comprising:
using a redox flow battery having a first chamber and a second chamber separated by a membrane, wherein the first chamber comprises a cathode and the second chamber comprises an anode;
conducting a first electrolyte as catholyte into the first chamber and conducting a second electrolyte as anolyte into the second chamber;
wherein the first electrolyte comprises a first reduction-oxidation pair and the second electrolyte comprises a second reduction-oxidation pair; and
the first electrolyte comprises a first pH-stabilizing buffer for chemically stabilizing the reduction-oxidation pair, the first buffer including glycine and sodium chloride;
the second electrolyte comprises a second pH-stabilizing buffer with at least one combination selected from the group consisting of: hydrochloric acid and potassium hydrogen phthalate, citric acid and sodium citrate, acetic acid and sodium acetate; and sodium hydroxide and sodium hydrogen phthalate; and
charging or discharging the redox flow battery.
|