| CPC G01S 19/27 (2013.01) [G01S 19/07 (2013.01); G06F 17/15 (2013.01); G06N 5/046 (2013.01)] | 24 Claims |
|
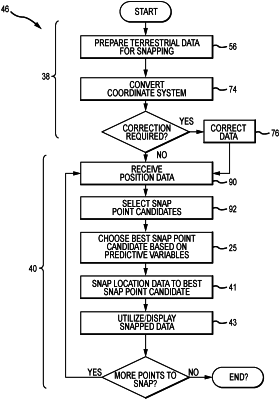
1. A method of correlating sensed position data with terrestrial features, the sensed position data comprising sensed position points, the terrestrial features being located by terrestrial data, comprising:
receiving the sensed position data from a position sensing system operatively associated with a moveable object;
selecting a reduced set of snap point candidates from the terrestrial data based on a sensed position point;
choosing a best snap point candidate from among the reduced set of snap point candidates based on a plurality of predictive variables and corresponding weighting factors for each snap point candidate in the reduced set of snap point candidates, wherein said choosing comprises
determining values of the predictive variables for each snap point candidate in the reduced set of snap point candidates;
obtaining the weighting factors for the predictive variables;
calculating a score for each snap point candidate in the reduced set of snap point candidates based on the values of the predictive variables and the corresponding weighting factors; and
identifying the best snap point candidate based on the calculated score; and
snapping the sensed position point to the best snap point candidate to produce a snapped position point, wherein said selecting, said choosing, and said snapping are performed in substantially real time so that said method correlates the sensed position data from the moveable object with terrestrial features in substantially real time.
|