| CPC G01R 31/085 (2013.01) [G01R 21/06 (2013.01); H02H 1/0007 (2013.01); H02H 3/387 (2013.01); H02H 7/22 (2013.01); H02H 1/0092 (2013.01); H02H 3/52 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
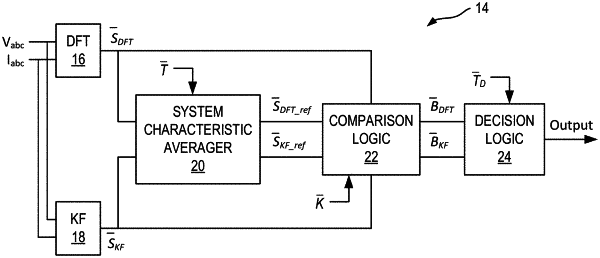
1. A high impedance fault (HIF) detector, comprising:
a system characteristic averager configured to store instantaneous power characteristic values and provide averaged power characteristic values of the instantaneous power characteristic values;
a decision circuit configured to determine occurrence of an HIF based on the instantaneous power characteristic values and the averaged power characteristic values; and
a Kalman filter configured to provide a first portion of the instantaneous power characteristic values to the system characteristic averager after filtering a received voltage signal and a received current signal, wherein the first portion of the instantaneous power characteristic values comprises at least one of an estimated in-phase component of a third harmonic of the received voltage signal (KFVa cos HV3, KFVb cos HV3, or KFVc cos HV3) or an estimated in-quadrature component of a third harmonic of the received voltage signal (KFVa sin HV3, KFVb sin HV3, or KFVc sin HV3);
wherein KF is a Kalman Filter coefficient, va is defined by a voltage of phase A, vb is defined by a voltage of phase B, and vc is defined by a voltage of phase C.
|