| CPC G01N 29/4418 (2013.01) [A61B 8/0883 (2013.01); A61B 8/485 (2013.01); A61B 8/5223 (2013.01); G01N 29/036 (2013.01); G01N 29/222 (2013.01); G01N 29/4436 (2013.01); G01N 29/4472 (2013.01); G01N 2291/014 (2013.01); G01N 2291/025 (2013.01); G01N 2291/02466 (2013.01); G01N 2291/02818 (2013.01); G01N 2291/02827 (2013.01); G01N 2291/0422 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
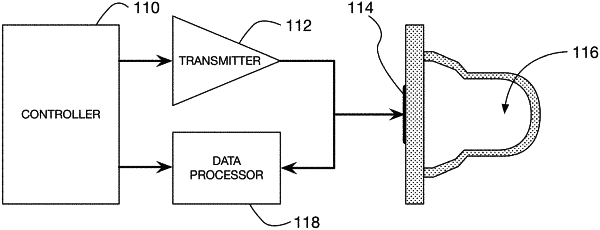
1. A method for characterizing a mechanical property of a test sample, the method comprising:
transmitting a plurality of waveforms into a test chamber, including at least one forcing waveform and at least two sensing waveforms;
receiving, via at least one transducer, at least two sensing waveforms from the test chamber corresponding to the at least two transmitted sensing waveforms;
estimating, by a processor, a resonance of the test sample from the at least two received sensing waveforms; and
determining, by the processor, a modulus value associated with stiffness of a clot formed of the test sample based on the estimated resonance; and
outputting, by the processor, a hemostatic parameter derived from the determined modulus value, wherein the outputted hemostatic parameter is used to evaluate and/or treat a hemostatic dysfunction.
|