| CPC H04L 45/127 (2013.01) [H04L 45/306 (2013.01); H04L 45/74 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
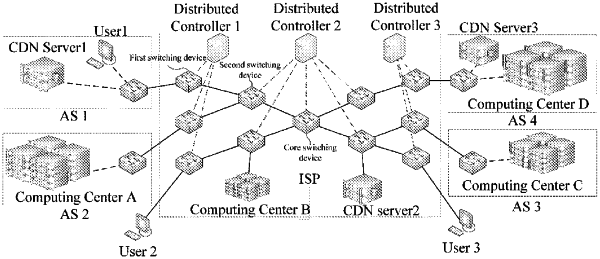
1. A method of computing power routing is characterized in that applied to a computing power routing scenario, wherein the computing power routing scenario includes at least a first switching device, a second switching device, a core switching device, a controller, and a computing power cluster, the computing power routing method comprising:
receiving a packet to be forwarded, wherein the packet to be forwarded includes an internet protocol (IP) message;
inserting network information of the first switching device in the IP message and re-encapsulating the packet to be forwarded to obtain the encapsulated packet, wherein the first switching device is a switching device receiving the packet to be forwarded;
the second switching device collects the network information in the encapsulated packets and sends the network information to the controller;
subscribing to the computing power cluster's computing power resource information and sending the computing power resource information to the controller;
the first switching device, the second switching device, and the core switching device construct a global network topology, wherein the global network topology includes multiple nodes;
using the network information to plan general routing tables for individual nodes;
using the network information and the computing power resource information to plan computing power routing tables for individual nodes; and
a request type in the packet to be forwarded matches a destination routing path for the packet to be forwarded, where the destination routing path is determined based on the general routing table or the computing power routing table.
|