| CPC G06F 3/0659 (2013.01) [G06F 3/0604 (2013.01); G06F 3/0673 (2013.01); G06F 12/06 (2013.01); G06F 2212/1016 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A data storage device, comprising:
a controller comprising computer-readable instructions that when executed by the controller, cause the controller to execute a method for command queue order adjustment, the method comprising:
read a first command comprising a first queue ID and a second command comprising a second queue ID from a host;
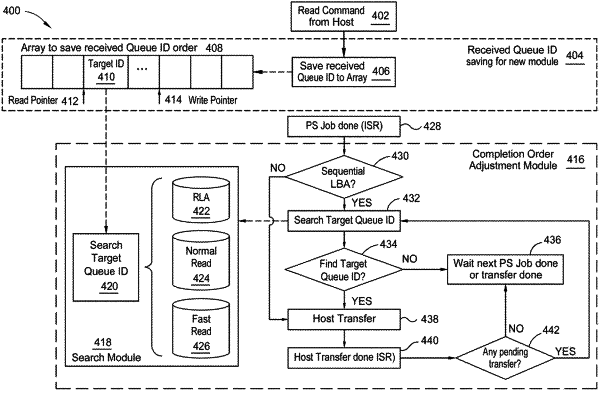
provide the first queue ID and the second queue ID to an array of a completion order adjustment module;
store the first queue ID and the second queue ID in the array;
provide the first command and the second command to a command handler for processing;
generate a first processed command and a second processed command, wherein the first processed command and the second processed command are processed in an order of a fast read to a read look ahead (RLA);
receive the first processed command at the completion order adjustment module;
determine if the first processed command is part of a logical block address (LBA) sequence of commands;
search the array for other commands of the sequence of commands;
wait to transfer until each command of the sequence of commands is found;
reorder the first queue ID and the second queue ID such that the first processed command comprising the first queue ID is sent to a host before the second processed command comprising the second queue ID is sent to the host;
transfer data associated with each command of the sequence of commands to the host;
generate a host transfer done interrupt service routine (ISR) and then check for any pending transfers; and
search a target queue ID when there are pending transfers, wherein the searching comprises using a search module to search a RLA location, a normal read location, and a fast read location, wherein the RLA location, the normal read location, and the fast read location are separate and distinct locations within the search module.
|