| CPC G01N 15/04 (2013.01) [C12Q 1/6816 (2013.01); C12Q 1/686 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
1. A method for analyzing targets comprising biological sample, the method comprising:
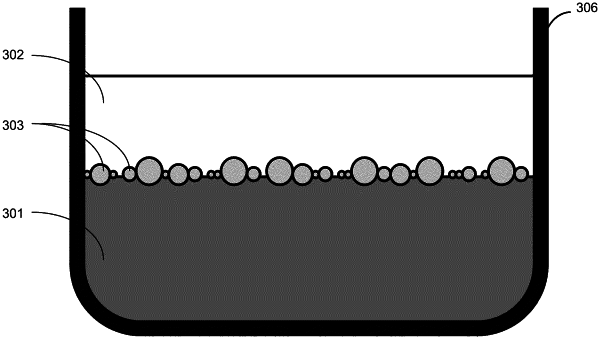
forming a volume, wherein the volume comprises a third phase in fluid communication with a first phase and a second phase and is within a field of view of an optical sensor, and an interface between the first phase and the second phase,
wherein the third phase is disposed along the interface,
wherein the third phase includes a plurality of targets comprising biological sample,
wherein the plurality of targets are disposed in a substantially non-overlapping single layer within the volume;
wherein the first phase and the second phase are liquids,
wherein the first phase has a first density, the second phase has a second density, and the third phase as a third density, wherein the first density, the second density, and the third density are different densities, and
wherein the first phase, the second phase, and the third phase are substantially immiscible,
amplifying the biological sample; and
imaging, using the optical sensor, the plurality of targets, to determine amplification of the biological sample.
|