| CPC F03G 7/0616 (2021.08) [B32B 15/01 (2013.01); B32B 15/013 (2013.01); F03G 7/0613 (2021.08); F03G 7/062 (2021.08); B33Y 80/00 (2014.12); F05C 2253/04 (2013.01)] | 8 Claims |
|
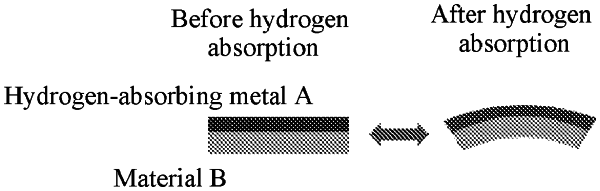
1. A method for preparing an adjustable deforming composite structure based on a hydrogen-induced expansion effect, wherein a composite is composed of a metal and a material, the metal has a hydrogen-absorbing expansion capability, and the material does not have the hydrogen-absorbing expansion capability or has a hydrogen-absorbing expansion capability less than the hydrogen-absorbing expansion capability of the metal under identical conditions, comprising:
preparing the adjustable deforming composite structure by a conventional metal preparation and processing method, the conventional metal preparation and processing method comprising at least one of rolling, forging, extrusion, diffusion welding, friction welding, and explosive cladding; or
preparing the adjustable deforming composite structure by a metal thin film preparation method, the metal thin film preparation method comprising at least one of chemical vapor deposition, physical vapor deposition, and electroplating; or
preparing the adjustable deforming composite structure by an additive manufacturing method, the additive manufacturing technology comprising at least one of powder-bed laser printing, electron beam selective melting, powder feeding laser or electron beam printing, electron beam freeform fabrication, binder jetting 3D printing, and powder stereolithography,
and further comprising:
additive manufacturing the material on a base under a hydrogen-containing atmosphere to obtain a hydrogen-containing composite structure;
or
using a hydrogen absorption on the metal as the base, and then additive manufacturing metal on the base under the hydrogen-containing atmosphere, to obtain the hydrogen-containing composite structure;
or
preparing a thin film of the metal on the material as the base under the hydrogen-containing atmosphere to obtain the hydrogen-containing composite structure;
or
using the hydrogen absorption on the metal as the base, and then preparing the thin film of the material under the hydrogen-containing atmosphere, to obtain the hydrogen-containing composite structure.
|