|
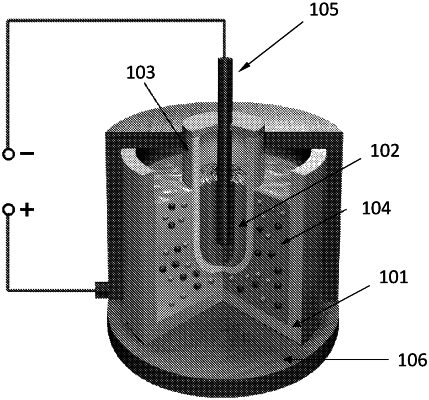
1. A method of one-step purification of lithium compounds, comprising electrolyzing a molten composition comprising a lithium salt and an aluminum salt, with an anode at least partially covered by metallic aluminum in contact with the molten composition and a cathode comprising molten lithium separated from the molten composition by a solid electrolyte capable of conducting lithium ions, wherein the solid electrolyte allows lithium ions, but not other atoms, to pass through, and comprises a garnet-type oxide comprises Li7-xLa3TaxZr2-xO12 wherein x is from 0.4 to 0.6, wherein the solid electrolyte has a relative density from 97% to 99.9%, and wherein after the electrolyzing, a concentration of lithium at the cathode is increased by from 7.2 times to over 1500 times at the molten composition.
|