| CPC C12P 33/06 (2013.01) | 20 Claims |
|
1. A process for the hydroxylation of the carbon atom 21 of a steroid, comprising the steps of:
(a) providing a cell expressing:
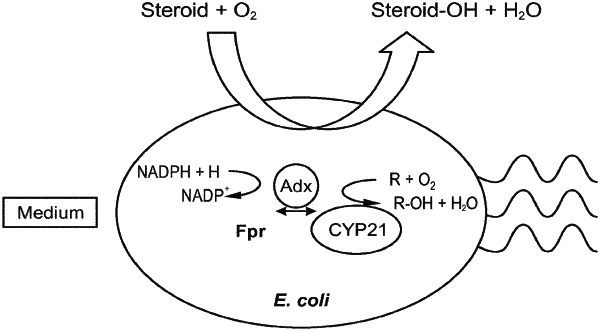
(i) a heterologous CYP21A2 protein or a functional variant thereof;
(ii) at least one heterologous electron transfer system capable of transferring electrons to CYP21A2, wherein the at least one electron transfer system is selected from the group consisting of:
the combination of a flavodoxin reductase (Fpr) and an adrenodoxin;
the combination of a Fpr and the ferredoxin domain of an electron transfer domain (etpfd);
the combination of an adrenodoxin reductase homolog (Arh) and an adrenodoxin; and
the combination of an Arh and etpfd; and
(iii) one or more chaperones facilitating folding of CYP21A2; and
(b) adding the steroid to the cell.
|