| CPC H04B 1/715 (2013.01) [H04W 72/535 (2023.01); H04W 72/542 (2023.01); H04B 2001/7152 (2013.01); H04B 1/7156 (2013.01); H04B 2201/692 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
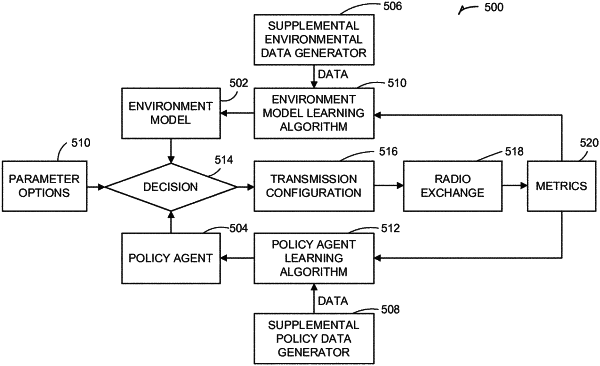
1. A wireless node configured to enhance one or more of power efficiency, interference immunity, packet latency, or packet throughput using dynamically-established link configurations, the wireless node comprising:
a transceiver configured to transmit and receive wireless communication via an antenna, the wireless node configured to receive wireless communication from a network manager; and
a cognitive engine configured to receive information regarding a network environment as input and, in response, generate transmission configuration data as output based on an environmental model tracking variances in the network environment;
wherein the wireless node is configured to generate a data communication for transmission by the transceiver to the network manager using the generated configuration data, and
wherein the generated configuration data includes transmission channel frequency and transmission data rate information.
|