| CPC H02J 3/0073 (2020.01) [H02J 3/003 (2020.01); H02J 3/08 (2013.01)] | 2 Claims |
|
1. A method for making a spatio-temporal combined optimal scheduling strategy of a mobile energy storage (MES) system, comprising the following steps:
step 1: inputting data of a power system, a traffic system, and an MES system, specifically comprising: a line parameter, load data, generator data, and a topological structure of the power system, a road parameter and a topological structure of the traffic system, a quantity of MES vehicles, a capacity of an MES battery, an upper limit of output active power, an upper limit of output reactive power, upper and lower capacity limits of the battery, charging and discharging efficiency of the battery, and an average traveling speed of an MES vehicle;
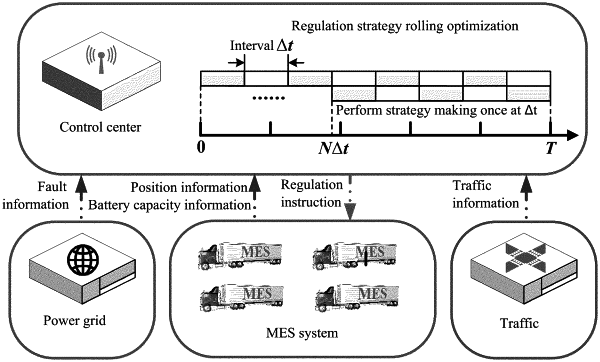
step 2: setting a time interval Δt, and initializing a time interval counter N to 0 and initial time t to 0;
step 3: inputting real-time fault, traffic, and MES data, specifically comprising: a position of a power line fault, expected repair time, a road congestion coefficient of the traffic system, and a real-time position and battery capacity of the MES vehicle;
step 4: optimizing and solving an optimal regulation model of the MES system, and delivering regulation decision instructions of the MES system, comprising a path instruction and a power instruction; regulate the MES system based on the regulation decision instructions; and
step 5: if the fault still exists after NΔt, setting N=N+1, and returning to step 3; otherwise, terminating a process of making a scheduling strategy.
|