| CPC C12Q 1/6825 (2013.01) [A61B 5/6867 (2013.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
1. A method of measuring a concentration of a target species in a sample by a process:
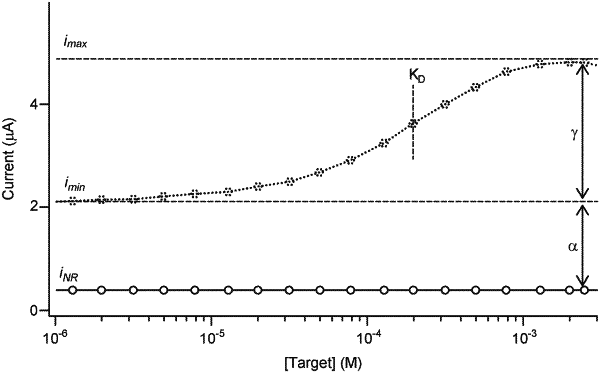
presenting the sample to an electrochemical sensor of a selected design, under a selected set of assay conditions; wherein the electrochemical sensor comprises a plurality of recognition elements bound to an electrode substrate; wherein each recognition element reversibly binds the target species; wherein one or more redox reporter species is associated with each recognition element; and wherein an output of the sensor, upon application of a suitable potential pulse, is a current comprising electron flow between the redox reporter species and the electrode substrate;
wherein a ratio of target-saturated output signal to target-free output signal is known for sensors of the selected design operated under the selected assay conditions;
wherein a ratio of signal output at a minimally-responsive frequency to target-free output signal is known for sensors of the selected design operated under the selected assay conditions;
performing a first interrogation comprising the application of a series of potential pulses to the sensor at a responsive pulse frequency to obtain an output value i, wherein the responsive frequency is a frequency which results in a sensor output that is dependent upon the concentration of the target species in the sample;
performing a second interrogation of the sample comprising the application of a series of potential pulses to the sensor at a minimally responsive pulse frequency to obtain an output value iNR; and
calculating the concentration of the target species by use of: i; iNR; the ratio of target-saturated output signal to target-free output signal; and the ratio of signal output at the minimally-responsive frequency to target-free output signal.
|