| CPC B29C 64/124 (2017.08) [B29C 64/393 (2017.08); B33Y 10/00 (2014.12); B33Y 50/02 (2014.12); B29C 64/282 (2017.08)] | 16 Claims |
|
1. A method of configuring an additive fabrication device to fabricate an object, the additive fabrication device configured to form the object from a plurality of layers of solid material by directing at least one source of actinic radiation onto a liquid photopolymer, the method comprising:
generating, using at least one processor, instructions that, when executed by the additive fabrication device, cause the additive fabrication device to fabricate the object at least in part by:
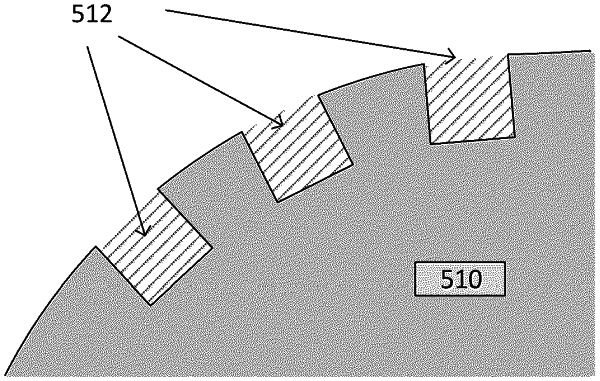
forming a first layer of the object according to a three-dimensional model of the object, wherein a first region of the first layer is cured by the at least one source of actinic radiation at a first exposure power, and wherein a second region of the first layer is cured by the at least one source of actinic radiation at a second exposure power, wherein the first region of the first layer comprises a plurality of notches around at least a portion of a perimeter of the first layer; and
forming a second layer of the object in contact with the first layer of the object, wherein at least a third region of the second layer overlaps a portion of the first region of the first layer, and wherein the third region of the second layer is cured with a greater cure depth than an adjacent region of the second layer, thereby directing additional actinic radiation to the portion of the first region of the first layer through the third region of the second layer.
|