| CPC A61N 1/36139 (2013.01) [A61N 1/025 (2013.01); A61N 1/0534 (2013.01); A61N 1/365 (2013.01); A61N 1/3956 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
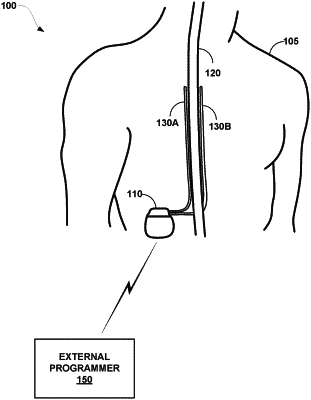
|
1. A system comprising:
a stimulation generator configured to deliver a stimulation pulse to a patient;
sensing circuitry configured to sense an evoked compound action potential (ECAP) signal evoked from the stimulation pulse; and
processing circuitry configured to:
determine a maximum value of a derivative of the ECAP signal;
determine a minimum value of the derivative of the ECAP signal;
determine a difference between the maximum value of the derivative and the minimum value of the derivative, wherein the difference is a characteristic value of the ECAP signal; and
determine, using the characteristic value of the ECAP signal, at least one electrical stimulation parameter value defining an electrical stimulation therapy to be delivered to the patient.
|