| CPC H03K 17/0828 (2013.01) [H03K 17/08128 (2013.01); H03K 17/0822 (2013.01); H03K 17/18 (2013.01)] | 9 Claims |
|
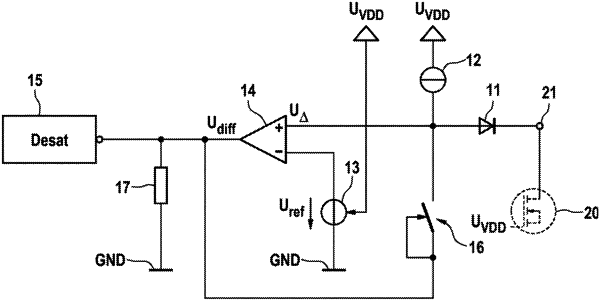
1. A method for short-circuit detection by saturation detection in power semiconductor switches, comprising the following steps:
providing (1) a reference voltage (Uref) depending on a supply voltage (UVDD) of a power semiconductor switch (20), with the result that the reference voltage (Uref) follows changes in the supply voltage (UVDD);
generating (2) a differential voltage (Udiff) which corresponds to a difference between a voltage drop (UΔ) across a load path of the power semiconductor switch (20) and the provided reference voltage (Uref);
comparing (3) the generated differential voltage (Udiff) with a predetermined limit voltage (Ulim), wherein a short-circuit current is detected in the load path of the power semiconductor switch (20) when the differential voltage (Udiff) exceeds the limit voltage (Ulim); and
opening (4) the power semiconductor switch (20) when a short-circuit current has been detected in the load path of the power semiconductor switch (20).
|