| CPC G10L 15/063 (2013.01) [G06N 20/00 (2019.01); G10L 21/0208 (2013.01); G10L 25/78 (2013.01); G10L 25/81 (2013.01); G10L 25/84 (2013.01); G10L 25/87 (2013.01); G10L 2025/783 (2013.01); G10L 2025/786 (2013.01)] | 16 Claims |
|
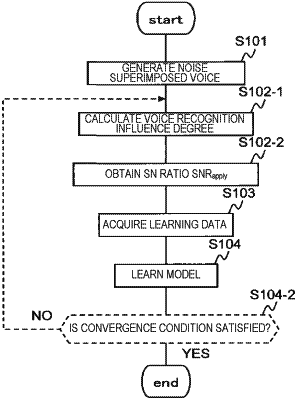
1. A learning data acquisition device comprising a processor configured to execute operations comprising:
determining an influence degree on voice recognition accuracy caused by a change of a signal-to-noise ratio, based on a result of voice recognition on kth noise superimposed voice data and a result of voice recognition on k−1th noise superimposed voice data, wherein K is an integer of 2 or larger, k=2, 3, . . . , K, and a signal-to-noise ratio of the kth noise superimposed voice data is smaller than a signal-to-noise ratio of the k−1th noise superimposed voice data;
obtaining a largest signal-to-noise ratio SNRapply among signal-to-noise ratios of the k−1th noise superimposed voice data when the influence degree meets a given threshold condition; and
acquiring noise superimposed voice data having a signal-to-noise ratio that is equal to or larger than the signal-to-noise ratio SNRapply, as learning data.
|