| CPC G06T 7/75 (2017.01) [G06T 1/0014 (2013.01); G06T 17/20 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20081 (2013.01)] | 10 Claims |
|
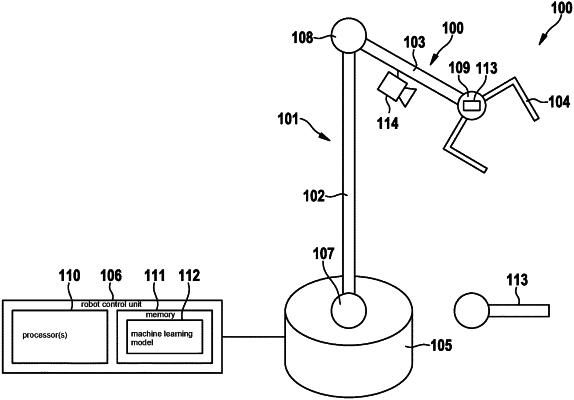
1. A method for ascertaining a pose of an object, comprising the following steps:
ascertaining a 3D model of the object, the 3D model including a grid of vertices;
recording a first camera image of the object from a first perspective;
recording a second camera image of the object from a second perspective, which differs from the first perspective;
ascertaining a correspondence between camera pixels of the first camera image and vertices of the 3D model;
ascertaining a correspondence between camera pixels of the second camera image and vertices of the 3D model; and
ascertaining the pose of the object from a set of poses by minimizing, across the set of poses, a loss function, the loss function for each pose being provided by:
projecting vertices of the 3D model into a respective camera image plane according to the first perspective, in the event that the 3D model is situated in the pose,
projecting vertices of the 3D model into a respective camera image plane according to the second perspective, in the event that the 3D model is situated in the pose,
calculating distance measures between the projections of the vertices projected according to the first perspective and the camera pixels of the first camera image, which are assigned to vertices projected according to the first perspective,
calculating distance measures between the projections of the vertices projected according to the second perspective and the camera pixels of the second camera image, which are assigned to the vertices projected according to the second perspective, and
accumulating the calculated distance measures to the loss function.
|