| CPC G06N 3/08 (2013.01) [G06N 3/04 (2013.01); G06N 3/045 (2023.01); H04W 4/02 (2013.01); H04W 4/023 (2013.01); H04W 4/38 (2018.02); H04W 4/40 (2018.02); H04W 4/90 (2018.02)] | 21 Claims |
|
1. A method comprising:
identifying, at a first wireless communication device, first raw data from a first sensor of a first wireless communication device;
identifying a second wireless communication device;
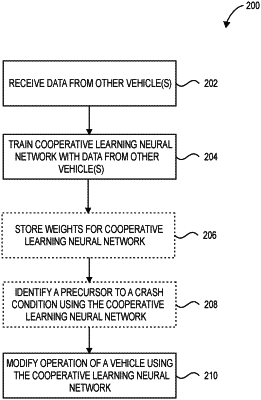
receiving, directly at the first wireless communication device, second raw data from a second sensor of the second wireless communication device, the second raw data received directly from the second wireless communication device in response to capture of the second raw data at the second sensor, where the second raw data is received at the first wireless communication device while the first wireless communication device is in communication with the second wireless communication device;
training one or more weights of a cooperative learning neural network, at the first wireless communication device using a combination of the first raw data and the second raw data received from the second sensor of the second wireless communication device, wherein the one or more weights are associated with one or more crash conditions or one or more objects, wherein, responsive to identifying that the second wireless communication device is within a threshold distance of the first wireless communication device, and responsive to the receiving of the second raw data, training the cooperative learning neural network at the first wireless communication device using the combination of the first raw data and the second raw data occurs while the second wireless communication device is within the threshold distance of the first wireless communication device, and training the cooperative learning neural network using the combination of the first raw data and the second raw data does not occur, otherwise;
detecting at least one crash condition or an object using the trained one or more weights; and
adjusting a speed or direction, or both, of the first wireless communication device responsive to identifying the at least one crash condition.
|