| CPC G06F 9/505 (2013.01) [G06F 9/4881 (2013.01); G06N 5/02 (2013.01); G06F 2209/5019 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
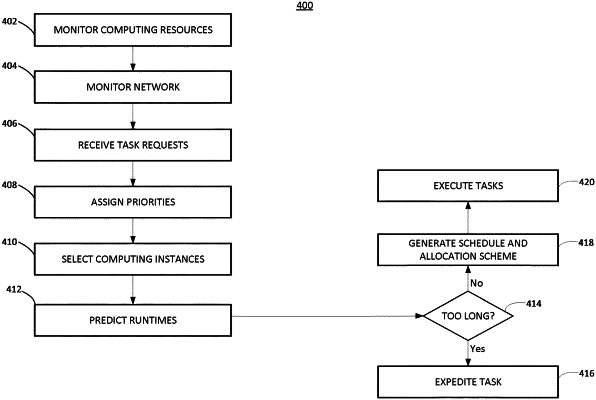
1. A method for executing a plurality of computing tasks, the method comprising:
receiving as containers, by an orchestration engine, task requests over a network from a plurality of process engines corresponding to respective machinery or devices, each task request indicating at least one real-time task requirement for executing a respective computing task of the plurality of computing tasks, the orchestration engine being included in a computing platform located remotely as compared to the process engines;
selecting a plurality of computing instances from a set of computing instances, the selected computing instances each having available computing resources, the computing instances being included in the computing platform and being in communication with the orchestration engine;
generating a predicted runtime for each of the computing tasks;
based on the predicted runtimes, task requirements, and available computing resources, determining a schedule and allocation scheme, the schedule and allocation scheme defining when each of the plurality of computing tasks is executed, and which of the plurality of selected computing instances executed each of the plurality of computing tasks;
executing, by the plurality of selected computing instances, the plurality of computing tasks according to the schedule and allocation scheme;
sending, by the orchestration engine, results of the executed computing tasks over the network to the process engines, to provide real-time control of the machinery or devices.
|