| CPC G06F 9/451 (2018.02) [G06F 9/542 (2013.01); G06F 11/302 (2013.01); G06F 11/3438 (2013.01); G06F 40/00 (2020.01); G06F 40/216 (2020.01); G06N 5/025 (2013.01); G06Q 10/06316 (2013.01); G06Q 10/0633 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
1. A computer-implemented method comprising:
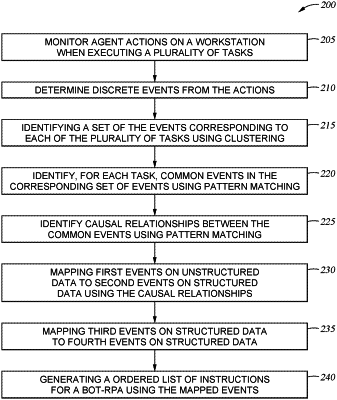
identifying events based on monitoring agent actions performed on a workstation when performing a task multiple times, wherein the identified events correspond to both unstructured and structured data sources, wherein identifying the events comprises:
assigning individual utterances in the unstructured data source as a first set of events,
identifying operating system (OS)-level events performed on the structured data source by monitoring actions of the OS in the workstation, and
identifying intra-application input/output (I/O) events performed on the structured data source by monitoring an I/O device used by the agent;
adding timestamps to the first set of events, the OS-level events, and the intra-application I/O events;
identify groupings of duplicate events in the identified events that each correspond to a common event using pattern matching;
identify causal relationships between the common events based on the timestamps;
mapping, based on at least one of the causal relationships, a first common event corresponding to the unstructured data source to a second common event corresponding to the structured data source; and
generating an ordered list of instructions for a robotic process automation (RPA) of a bot based on the mapped events.
|