| CPC G06F 40/279 (2020.01) [G06F 18/2113 (2023.01); G06F 18/22 (2023.01); G06F 40/137 (2020.01); G06V 30/414 (2022.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A computer-implemented method comprising:
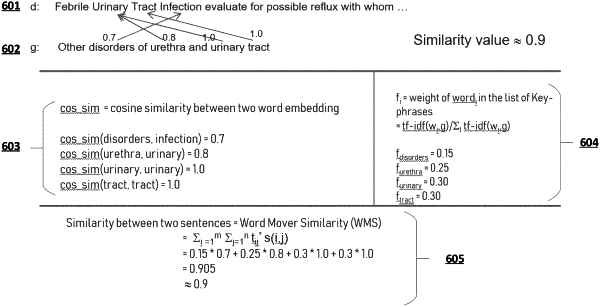
generating, using one or more processors, a maximal word similarity score for a reference text data object and a target text data object, wherein: (i) the maximal word similarity score describes a maximal value of a transition cost value indicative of a measure of cost to transform a first embedded representation associated with one or more target words of the target text data object into a second embedded representation associated with one or more reference words of the reference text data object, and (ii) the transition cost value is determined based at least in part on, for each word pair comprising a reference word and a target word, a word-wise flow value and, a word-wise similarity value;
generating, using the one or more processors, a predicted similarity score for the reference text data object and the target text data object based at least in part on the maximal word similarity score; and
initiating, using the one or more processors, the performance of one or more prediction-based actions based at least in part on the predicted similarity score.
|