| CPC G06F 12/0802 (2013.01) [G06F 3/0619 (2013.01); G06F 3/0655 (2013.01); G06F 3/0679 (2013.01); G06F 2212/60 (2013.01); G06F 2212/7201 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A system comprising:
a volatile memory device;
a non-volatile memory device; and
a processing device, operatively coupled with the volatile and non-volatile memory devices, to perform operations comprising:
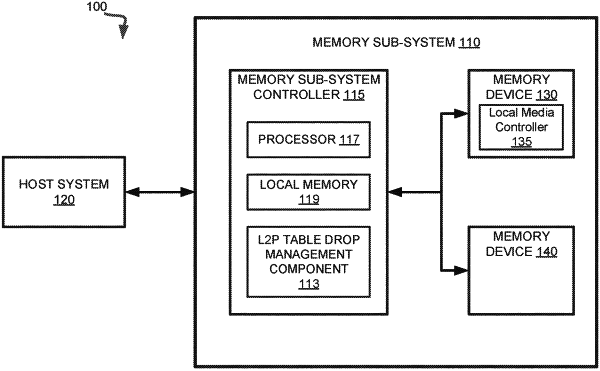
maintaining a logical-to-physical (L2P) table, wherein a plurality of sections of the L2P table is cached in the volatile memory device;
maintaining a total dirty count for the L2P table, wherein the total dirty count comprises a total number of updates to the L2P table;
maintaining, for the plurality of sections, respective section dirty counts, wherein each respective section dirty count comprises a total number of updates to a corresponding section;
determining that the total dirty count for the L2P table satisfies a threshold criterion;
in response to determining that the total dirty count for the L2P table satisfies the threshold criterion, identifying, based on the respective section dirty counts, a first section of the plurality of sections with a highest section dirty count; and
writing the first section of the L2P table to the non-volatile memory device.
|