| CPC G01S 19/21 (2013.01) [H04B 1/1027 (2013.01); H04B 1/109 (2013.01); H04K 3/228 (2013.01); H04K 3/90 (2013.01)] | 7 Claims |
|
1. A system comprising:
an antenna that receives signals, wherein the signals comprise a weak portion associated with one or more GNSS satellites and a strong interference portion from an interfering signal source;
GNSS interference rejection circuitry comprising:
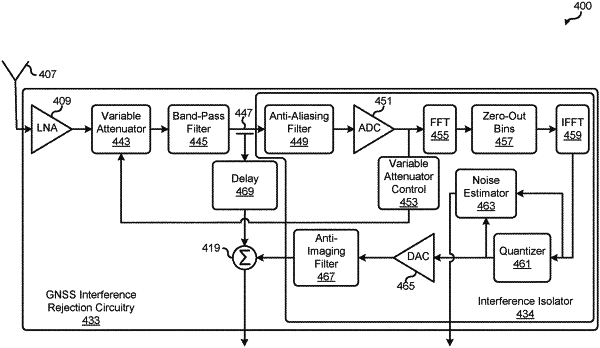
an interference isolator that receives the received signals and provides an estimated strong interference portion as a first output and a quantization noise estimate as a second output, wherein the interference isolator is configured to:
convert the received signals into digital signals;
execute a fast Fourier transform on a digital signal in the digital signals;
remove the weak portion of the digital signal from the digital signal to create the estimated strong interference portion by setting frequency bins of the transformed digital signal to zero that have a signal power less than a power level threshold, wherein the power level threshold is set based on at least one of a threshold percentage of a signal component having a largest magnitude, and an expected highest magnitude for a GNSS signal; and
execute an inverse fast Fourier transform on the estimated strong interference portion;
quantize the estimated strong interference portion to a number of bits used by a digital-to-analog converter;
estimate the noise introduced into the estimated strong interference portion by quantization to generate the quantization noise estimate; and
convert the quantized estimated strong interference portion to an analog estimated strong interference portion;
a summer that subtracts the analog estimated strong interference portion from the received signals to create a summed signal; and
a local noise remover that converts the summed signal into a digital summed signal and subtracts the quantization noise estimate from the digital summed signal; and
a GNSS receiver coupled to receive the digital summed signal from the GNSS interference rejection circuitry as produced by the local noise remover.
|