| CPC G01N 29/07 (2013.01) [G01N 29/11 (2013.01); G06N 3/08 (2013.01); G01N 2291/101 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
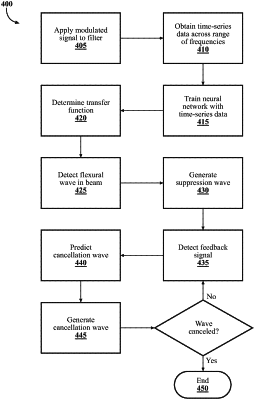
1. A flexural wave absorption system, comprising:
a sensor configured to be connected to a beam;
an actuator configured to be connected to the beam;
a processor; and
a memory communicably coupled to the processor and storing:
a wave module including instructions that when executed by the processor cause the processor to:
determine an amplitude and a phase of an incident wave propagating in the beam based on a signal from the sensor; and
control the actuator to generate a suppression wave, based on the amplitude and the phase of the incident wave; that reduces a coefficient of reflection of the incident wave resulting in a reflected wave; and
a neural network module including instructions that when executed by the processor cause the processor to:
determine that a sampling rate of the sensor is less than a threshold;
cause in response to a determination that the sampling rate is less than the threshold, a time delay to be imposed on a feedback signal input into a neural network to predict a voltage Va to apply to the actuator to generate a cancellation wave, wherein the feedback signal is received from the sensor; and
control the actuator to generate the cancellation wave based on the time-delayed feedback signal that indicates multiple wave components present in the beam, the multiple wave components including the incident wave, the suppression wave, and the reflected wave.
|