| CPC G01N 21/645 (2013.01) [C12Q 1/6851 (2013.01); G01N 21/278 (2013.01); G01N 21/6428 (2013.01)] | 24 Claims |
|
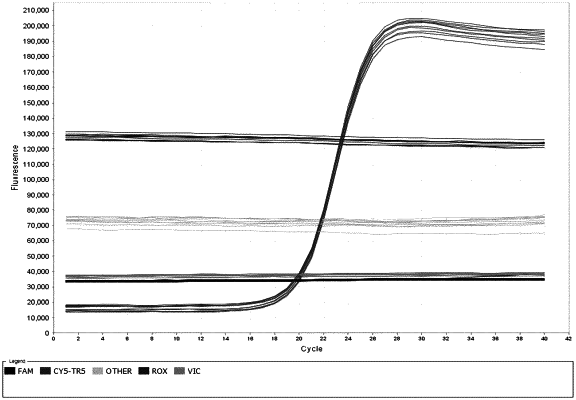
1. A method for reducing a false positive measurement in a biological sample using a multispectral analysis system, the method comprising:
calibrating the system using a first signal from a first calibration region of a calibration sample, wherein the calibration sample comprises a plurality of calibration regions on a substrate, and wherein the plurality of calibration regions comprises:
the first calibration region corresponding to a first fluorescent entity, wherein the first calibration region comprises a concentration of the first fluorescent entity in the first calibration region that is larger than a non-zero concentration of a second fluorescent entity in the first calibration region, wherein a fraction of the second fluorescent entity in the first calibration region relative to a total amount of the first and second fluorescent entities in the first calibration region is between 0.02 and 0.08, and wherein said concentration of the first fluorescent entity in the first calibration region and said fraction are configured to reduce spectral cross-talk of the fluorescence emission of the first fluorescent entity in the biological sample into a spectral emission channel for the second fluorescent entity in the biological sample;
measuring a fluorescence emission from the biological sample, wherein the fluorescence emission comprises a first measurement from the first fluorescent entity in the biological sample; and
reducing the false positive measurement arising from spectral cross-talk from the first fluorescent entity in the biological sample into the spectral emission channel for the second fluorescent entity in the biological sample by correcting the first measurement from the biological sample with the first signal from the first calibration region.
|