| CPC E21B 43/267 (2013.01) | 3 Claims |
|
1. A diverting agent, comprising:
a powder-like polyvinyl alcohol-based resin (P1); and
a pellet-like polyvinyl alcohol-based resin (P2), wherein
the diverting agent has an adsorption coefficient kc of 0.01 or more and 1 or less, and the adsorption coefficient kc is obtained by (i) to (iii),
(i) the diverting agent is added to a 0.6 mass % aqueous solution of guar gum to prepare a mixed solution having a diverting agent concentration of 6 mass %, and the mixed solution is dispersed at 23° C. for 30 minutes to obtain a dispersion, and the dispersion is pressurized and dehydrated at a pressure of 0.4 MPa using a pressure dehydration device equipped with a slit-shaped drainage unit, and an integrated dehydration amount y with respect to a square root x of time is calculated, and a regression line represented by Equation (A) calculated by the least squares method is obtained from a scatter diagram plotted on a graph in which a horizontal axis is the square root x of time and a vertical axis is the integrated dehydration amount y, in which
y=ax+b, and Equation (A)
in Equation (A), y represents the integrated dehydration amount (grams), and x represents the square root of time (minutes) elapsed from a start of pressurization, and a and b represent a slope and an intercept of the regression line, respectively, and 0<x≤2,
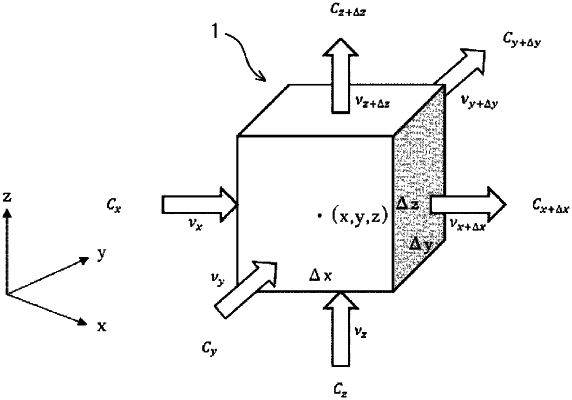
(ii) filling of the slit-shaped drainage unit in the pressure dehydration device with the diverting agent is presumed to be plugging caused by adsorption and filling of the powder-like polyvinyl alcohol-based resin (P1) into pores formed by bridging to slits of the pellet-like polyvinyl alcohol-based resin (P2), and an adsorption term r represented by Equation (5) is introduced into an advection equation used for numerical simulation of the filling, in which
r=kc(1−Φ0)C, and Equation (5)
in Equation (5), kc represents the adsorption coefficient, and Φ0 represents a porosity (%) of the pores formed by the pellet-like polyvinyl alcohol-based resin (P2), and C represents a concentration (mass %) of the powder-like polyvinyl alcohol-based resin (P1) in the dispersion, and
(iii) the adsorption coefficient kc is obtained so that the advection equation into which the adsorption term r is introduced matches Equation (A).
|