| CPC C10L 5/44 (2013.01) | 6 Claims |
|
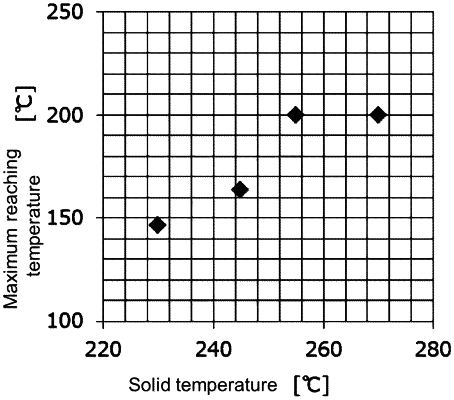
1. A biomass solid fuel which is obtained by molding a pulverized biomass into unheated biomass blocks and heating the unheated biomass blocks at a temperature of 230° C. to 270° C., wherein mutual bonding or adhesion between pulverized biomass particles is maintained after immersion in water, and which has a maximum reaching temperature of less than 200° C. in a self-heating property test in which the biomass solid fuel is charged into a sample container placed in an oven at a temperature of 140° C., and the temperature of the biomass solid fuel is continually measured for 24 hours during which the highest temperature thereof is defined as the maximum reaching temperature, and wherein at least one condition selected from the group consisting of the following conditions, (d1) and (e1) is satisfied:
condition (d1): a raw material of the pulverized biomass comprises Pinus radiata, and the biomass solid fuel has a volatile matter (dry ash free basis) of 77.5 wt % or more; and
condition (e1): a raw material of the pulverized biomass comprises a mixture of larch, spruce and birch, and the biomass solid fuel has a volatile matter (dry ash free basis) of 71.0 wt % or more.
|