| CPC B01L 3/5025 (2013.01) [B01L 3/50273 (2013.01); B01L 2200/00 (2013.01); B01L 2300/0816 (2013.01); B01L 2300/161 (2013.01); B01L 2300/165 (2013.01); B01L 2400/0406 (2013.01); B01L 2400/0481 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
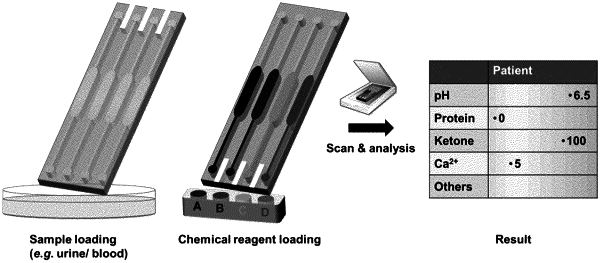
1. A method of testing a fluid droplet sample for an analyte, the method comprising the steps of:
providing a biochemical analysis system comprising multiple inlet channels and one or more chambers for mixing and reaction of the fluid droplet sample, each of the multiple inlet channels having a non-fouling, slippery surface, each of the multiple inlet channels including a first end, which is open and exposed, and a second end connected to the one or more chambers, each of the multiple inlet channels tapering from one of the first and second ends to the other of the first and second ends at a converging or diverging angle;
loading the biochemical analysis system with the fluid droplet sample;
autonomously transporting the fluid droplet sample to the one or more chambers by a geometry of each of the multiple inlet channels and without any external power source including pipettes, pumps, and magnetic and electric forces; and
detecting whether the analyte is present in the fluid droplet sample.
|