| CPC A61N 1/36139 (2013.01) [A61B 5/24 (2021.01); A61N 1/36062 (2017.08); A61N 1/36128 (2013.01); A61N 1/36132 (2013.01); A61N 1/36153 (2013.01); A61N 1/36171 (2013.01); A61N 1/36175 (2013.01); A61N 1/36192 (2013.01); A61N 1/37235 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
9. A device for providing electrical stimulation to a patient using an electrode lead implanted in the patient, wherein the electrode lead comprises a plurality of electrodes, the device comprising:
a microprocessor programmed to:
cause a first one or more of the electrodes to issue electrical stimulation to the patient's neural tissue,
cause a second one or more of the electrodes to record electrical signals in the patient's neural tissue, wherein the electrical signals comprise action potentials evoked by neural populations recruited by the stimulation,
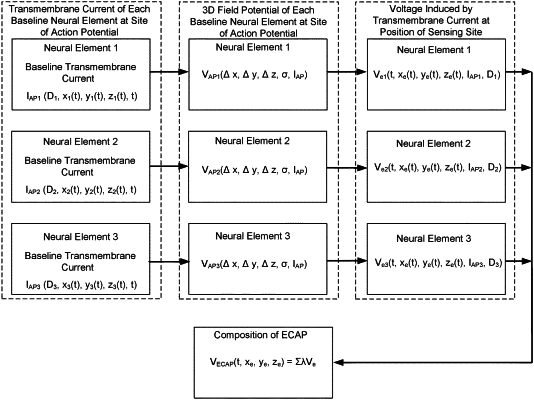
decompose the recorded electrical signals to determine contributions of one or more of the recruited neural populations to the recorded electrical signals by comparing the recorded electrical signals to modeled neural responses derived from a model, wherein the model comprises:
a plurality of modeled neural elements and a weight associated with each of the modeled neural populations, and
wherein the modeled neural responses comprise a weighted summation of modeled action potentials evoked in the modeled neural populations by the stimulation waveform, and
use the determined contributions to adjust the stimulation.
|