| CPC A61N 1/36128 (2013.01) [A61B 5/02108 (2013.01); A61B 5/316 (2021.01); A61B 5/318 (2021.01); A61B 5/369 (2021.01); A61B 5/398 (2021.01); A61B 5/4812 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A method for enhancing slow wave activity (SWA), comprising:
receiving a plurality of bio-signals from a user;
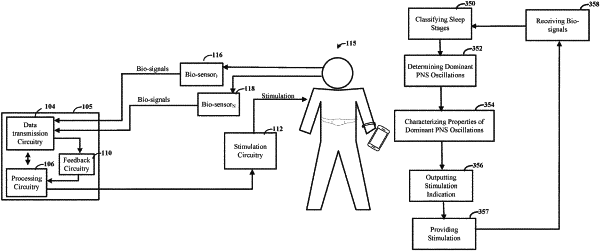
classifying sleep stages using the plurality of bio-signals;
determining a dominant oscillation in a peripheral nervous system (PNS) bio-signal of the plurality of bio-signals as a function of time and the sleep stages by:
calculating a power spectral density (PSD) indicative of oscillations in the PNS bio-signal, and
detecting a peak in the PSD as the dominant oscillation,
wherein the dominant oscillation is a rhythm of the PNS bio-signal occurring at a dominant frequency, the dominant frequency including a frequency of the PSD at the peak, and wherein the PNS bio-signal is selected from the group consisting of:
blood pressure, heart rate, breathing, a pulse wave, and a combination thereof;
characterizing a property of the dominant oscillation including at least one of a phase, a phase shift, an amplitude, and a frequency of the dominant oscillation by:
decomposing the PNS bio-signal in the dominant frequency as a function of time using a filter to filter out frequency content other than the dominant frequency and identifying the property from the decomposed PNS bio-signal;
providing an indication of an optimal window, based on timing of the property as characterized from the decomposed PNS bio-signal for maximizing SWA generation, to stimulation circuitry configured and arranged to deliver stimulation to the user within the optimal window, wherein the optimal window is selected based on data indicating stimulation improves electroencephalogram (EEG) SWA within the user during the optimal window, the data comprising past observed responses to prior stimulation including measures of EEG and the PNS bio-signal; and
providing feedback responsive to the stimulation based on an EEG signal of the user.
|