| CPC A61B 5/11 (2013.01) [A61B 5/0077 (2013.01); A61B 5/1176 (2013.01); A61B 5/4064 (2013.01); A61B 5/746 (2013.01); G06F 18/22 (2023.01); G06T 7/0012 (2013.01); G06T 7/0016 (2013.01); G06T 7/20 (2013.01); G06T 7/292 (2017.01); G06T 11/60 (2013.01); G06V 20/52 (2022.01); G06V 20/647 (2022.01); G06V 40/172 (2022.01); G06V 40/20 (2022.01); G08B 5/22 (2013.01); G08B 13/196 (2013.01); G08B 21/182 (2013.01); G08B 25/009 (2013.01); G16H 10/60 (2018.01); G16H 15/00 (2018.01); G16H 20/10 (2018.01); G16H 30/20 (2018.01); G16H 40/20 (2018.01); G16H 40/63 (2018.01); G16H 40/67 (2018.01); G16H 50/30 (2018.01); G16H 80/00 (2018.01); H04N 7/18 (2013.01); H04N 7/181 (2013.01); H04N 7/183 (2013.01); H04N 13/204 (2018.05); H04N 13/207 (2018.05); H04N 23/63 (2023.01); G06F 3/0482 (2013.01); G06F 3/04847 (2013.01); G06T 2200/04 (2013.01); G06T 2200/24 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10012 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10021 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10024 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20221 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30201 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30232 (2013.01); G06V 40/161 (2022.01); G08B 13/19639 (2013.01); G08B 21/0476 (2013.01); H04N 2013/0085 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
1. A computerized method for detecting stroke symptoms comprising:
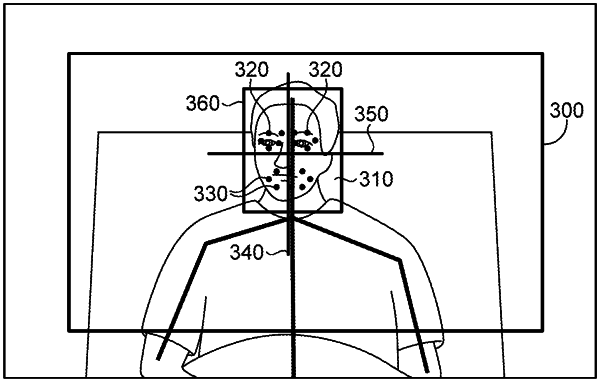
capturing image data including two or more images including a face of a person using at least one 3-dimensional (3D) sensor;
superimposing at least one axis of a 3-dimensional (3D) axis system at a reference anatomical feature of the face in a portion of the image data including the face of the person; and
communicating an electronic alert to a remote device in response to detecting an asymmetric change in position of at least one reference point of a plurality of reference points that correspond to anatomical features on the face of the person within the image data relative to the 3D axis system, wherein the detected asymmetric change in position of the at least one reference point represents a change in a degree of asymmetry corresponding to a depth axis in the 3D axis system, and wherein the change in the degree of asymmetry exceeds a threshold change of about 10% or 3 mm in the degree of asymmetry.
|