| CPC G16B 30/20 (2019.02) [C12Q 1/6874 (2013.01); G16B 30/00 (2019.02)] | 14 Claims |
|
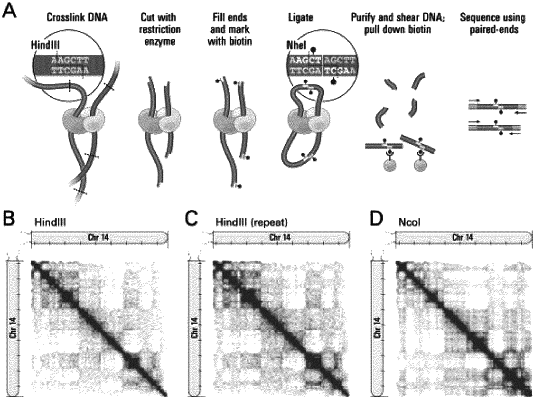
1. A method for haplotype phasing, the method comprising:
providing a cell comprising chromosomes;
crosslinking DNA within the chromosomes to form crosslinked DNA;
fragmenting the crosslinked DNA to form fragmented crosslinked DNA;
ligating two regions of the fragmented crosslinked DNA that are in close physical proximity to create ligated DNA comprising a ligation product, wherein the two regions comprise an intra-chromosomal pair;
shearing the ligated DNA to generate a plurality of smaller genomic fragments;
sequencing the plurality of smaller genomic fragments to generate sequencing reads;
identifying at least one heterozygous site in the sequencing reads; and
using the sequencing reads to determine haplotype phasing of the at least one heterozygous site.
|